If you love chocolate, chances are the cocoa beans that made it came from Africa. The continent produces more than 70% of the world’s cocoa, with countries like Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, and Cameroon leading the way. But what makes African cocoa so special? Why do chocolate makers and food manufacturers across the world rely on it?
Think of any chocolate product—chocolate bars, ice cream, cakes, spreads like Nutella, or even cocoa powder for baking. Chances are, it has African cocoa in it.
Mass-market chocolate brands like Cadbury, Nestlé, and Hershey’s depend on West African cocoa. Even luxury chocolate brands blend African beans with other premium varieties for a richer taste. Cocoa butter, which is extracted from cocoa beans, is also widely used in cosmetics, lotions, and even medicines.
This level of demand is why African cocoa will always be important in the global market.
The Flavor Profile: A Taste of Africa
One of the biggest reasons African cocoa beans are in such high demand is their unique flavor profile. Cocoa beans from Africa are known for their rich, bold, and complex flavors, which chocolate makers love to work with.
The flavor of chocolate depends on the cocoa beans used. African cocoa beans, especially those from Ivory Coast and Ghana, are known for their deep, rich, and bold chocolatey taste. This is why big chocolate brands prefer them—they provide that classic chocolate flavor people love.
Ivory Coast and Ghana produce beans with a slightly bitter, deep cocoa taste, making them perfect for dark chocolate. Meanwhile, Nigerian and Cameroonian cocoa beans have fruity and nutty notes, making them great for milk chocolate and premium chocolate products.
Chocolate makers often mix different beans to create unique flavors, but African cocoa is the base ingredient for most chocolates you see in stores. It’s reliable, high-quality, and works well in all kinds of recipes.
-
- Ivory Coast and Ghana: These two countries are the powerhouses of cocoa production, contributing over 60% of the world’s supply. Cocoa from this region is often described as having a strong, earthy flavor with hints of fruit and nuts. It’s versatile and works well in everything from dark chocolate to milk chocolate.
-
- Nigeria: Nigerian cocoa beans are slightly different, offering a more intense, almost smoky flavor. This makes them ideal for dark chocolate and gourmet products where a robust taste is desired.
-
- Cameroon: Cameroonian cocoa is known for its balanced flavor—sweet, fruity, and slightly acidic. It’s a favorite among artisanal chocolate makers who want to create unique, high-end products.
These distinct flavors are a result of the region’s climate, soil, and farming practices. The tropical weather, with its consistent rainfall and humidity, creates the perfect conditions for cocoa trees to thrive. The soil in these regions is rich in minerals, which adds depth to the flavor of the beans.
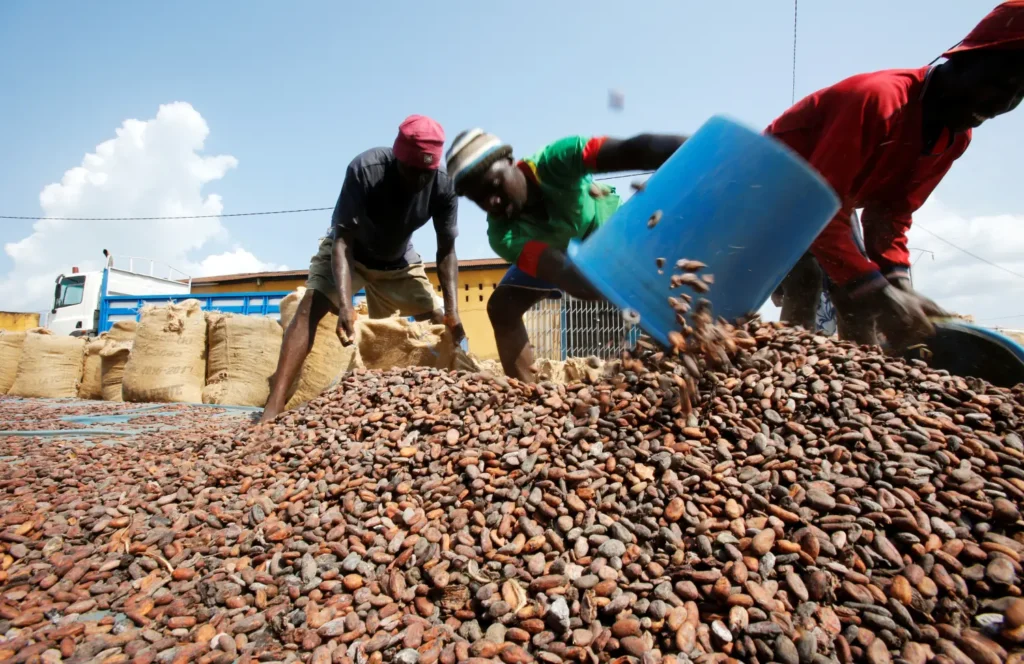

Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
In recent years, there’s been a growing demand for sustainably sourced cocoa, and African countries are stepping up to meet this need. Many cocoa farmers in Africa are adopting sustainable farming practices to protect the environment and ensure the long-term viability of their crops.
-
- Fair Trade Certification: Ghana and Ivory Coast have been at the forefront of the fair trade movement, ensuring that farmers receive fair wages and work under ethical conditions. This not only improves the livelihoods of farmers but also attracts buyers who prioritize ethical sourcing.
-
- Environmental Initiatives: Programs like the Cocoa & Forests Initiative (CFI) in Ivory Coast and Ghana aim to end deforestation and promote agroforestry, where cocoa is grown alongside other trees to preserve biodiversity.
-
- Traceability: Many African cocoa producers are investing in traceability systems, allowing buyers to track the journey of their cocoa beans from farm to factory. This transparency builds trust and appeals to consumers who want to know the origin of their chocolate.
These efforts are making African cocoa more attractive to global buyers who are increasingly conscious of the environmental and social impact of their supply chains.
Quality and Consistency
African cocoa beans are known for their high quality and consistency, which are critical for large-scale chocolate production.
-
- Fermentation and Drying: The post-harvest processing of cocoa beans—fermentation and drying—is done with great care in Africa. Proper fermentation is essential for developing the beans’ flavor, and African farmers have mastered this art over generations.
-
- Grading Systems: Countries like Ghana have strict grading systems to ensure that only the best beans make it to the market. For example, Ghana’s Cocoa Board (Cocobod) oversees the quality of cocoa exports, ensuring that they meet international standards.
-
- Reliability: Because of the scale of production and established infrastructure, buyers can rely on African cocoa beans to meet their quality and quantity requirements consistently.
Scale of Production: Africa Produces Cocoa at a Massive Scale
When it comes to cocoa production, Africa is the undisputed leader. Ivory Coast and Ghana alone produce more cocoa than the rest of the world combined. This massive scale of production makes African cocoa beans not only abundant but also more accessible and affordable for buyers.
Also, cocoa trees need warm temperatures, regular rainfall, and rich soil—which is exactly what West Africa offers. The region is located in the tropical belt, meaning the climate is ideal for cocoa all year round.
In places like Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, and Ivory Coast, cocoa farmers don’t have to rely on artificial farming techniques. The natural environment does most of the work, making African cocoa more organic and natural compared to some other regions.
-
- Ivory Coast alone produces over 2 million metric tons of cocoa every year.
-
- Ghana follows with around 800,000–900,000 metric tons.
-
- Nigeria and Cameroon together contribute around 500,000 metric tons.
With this kind of scale, chocolate manufacturers know they can always depend on Africa to supply the beans they need. No other region comes close to producing as much cocoa.
Challenges and Opportunities
While African cocoa is in high demand, the industry faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its continued success.
-
- Low Farmer Income: Despite the high demand for cocoa, many farmers in Africa live in poverty. Efforts are being made to improve farmer incomes through fair trade practices and government support.
-
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns threaten cocoa production. Farmers are adopting climate-resilient practices, but more support is needed to mitigate these risks.
-
- Diversification: Some African countries are exploring ways to add value to their cocoa by processing it locally instead of exporting raw beans. This could create more jobs and increase revenue for producing countries.
The Future of African Cocoa Looks Strong
Despite challenges like climate change, fluctuating prices, and sustainability concerns, the demand for cocoa keeps growing. Consumers are eating more chocolate than ever, and new markets in China, India, and the Middle East are increasing demand.
Some key trends shaping the future of African cocoa include:
-
- Premium & Organic Cocoa: More African countries are producing high-end, organic cocoa to meet growing demand.
-
- Technology in Cocoa Farming: Digital platforms help farmers monitor soil quality, weather conditions, and market prices.
-
- Direct Trade Models: Chocolate brands are working directly with African farmers to ensure better quality and fairer prices.
Africa’s cocoa industry is evolving, but one thing is certain—it will remain the world’s top cocoa supplier for years to come.
Conclusion
So why is African cocoa in such high demand? It’s simple.
-
- It has the best flavors for making chocolate.
-
- It’s produced at a massive scale, ensuring a steady supply.
-
- The climate is perfect for growing cocoa naturally.
-
- Almost every chocolate product contains African cocoa.
-
- Sustainability programs are making it more ethical and fair for farmers.
-
- It supports millions of people across Africa.
From the chocolate bars we eat to the cocoa powder in our kitchens, African cocoa is everywhere. And with rising demand for chocolate worldwide, it’s only going to become more valuable.
The next time you enjoy a piece of chocolate, just remember—it probably started as a cocoa bean in Africa.
FAQs
-
- Which African country produces the most cocoa?
Ivory Coast is the largest cocoa producer in the world, followed by Ghana, Nigeria, and Cameroon.
-
- Why do chocolate companies prefer African cocoa?
African cocoa has a rich, deep flavor, is produced in large quantities, and is essential for making high-quality chocolate.
-
- Is African cocoa used in luxury chocolates?
Yes! While some premium brands blend it with beans from South America, African cocoa is still the base for most chocolates.
-
- What are the challenges in the African cocoa industry?
Fluctuating cocoa prices, climate change, and ethical concerns like child labor and deforestation are key challenges.
-
- What’s the future of African cocoa?
With increasing demand for chocolate and sustainable farming improvements, African cocoa will remain the backbone of the global chocolate industry.







2 Responses
I am extremely inspired with your writing talents as well as with the structure
on your weblog. Is that this a paid subject matter or did you modify it yourself?
Anyway stay up the nice high quality writing, it’s rare to see a
great blog like this one nowadays. Beacons AI!
Nice