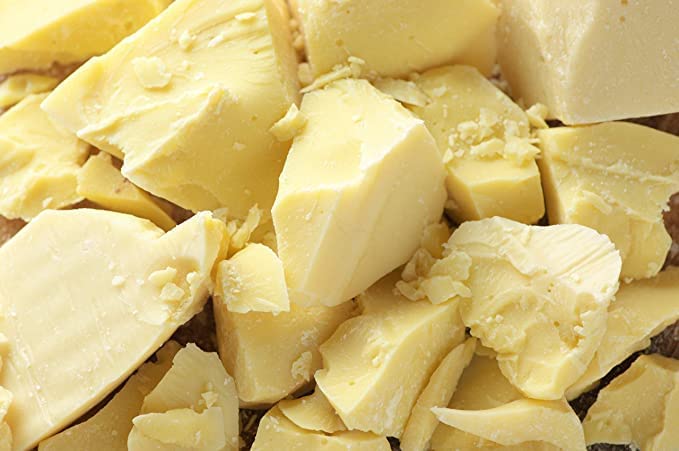
Cocoa butter is one of the most valuable products derived from the cocoa bean. Known for its pale-yellow color, mild chocolate aroma, and smooth texture, cocoa butter is a key ingredient in the global food industry. It is the fat extracted from cocoa beans during the chocolate-making process and is widely used in chocolates, confectionery, baked goods, and premium food applications.
In food production, cocoa butter plays a critical role because of its unique melting properties. Unlike many vegetable fats, cocoa butter melts precisely at body temperature, giving chocolate its distinctive “melt-in-the-mouth” quality. This property, combined with its natural stability and rich flavor, makes it indispensable for chocolatiers and food manufacturers worldwide.
Africa, particularly Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire, remains the largest source of premium cocoa butter due to its superior cocoa beans. With global food markets expanding, regions such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar are becoming major destinations for cocoa butter imports in the GCC regions, reflecting both the rising consumption of chocolates and the growth of the wider confectionery sector.
The price of cocoa butter continues to reflect its premium status. As of current market reports, Africa-origin premium cocoa butter is priced at around 22,000 USD per metric ton (FOB, Ghana), highlighting its value as a sought-after food ingredient.
How Cocoa Butter is Produced for Food Use
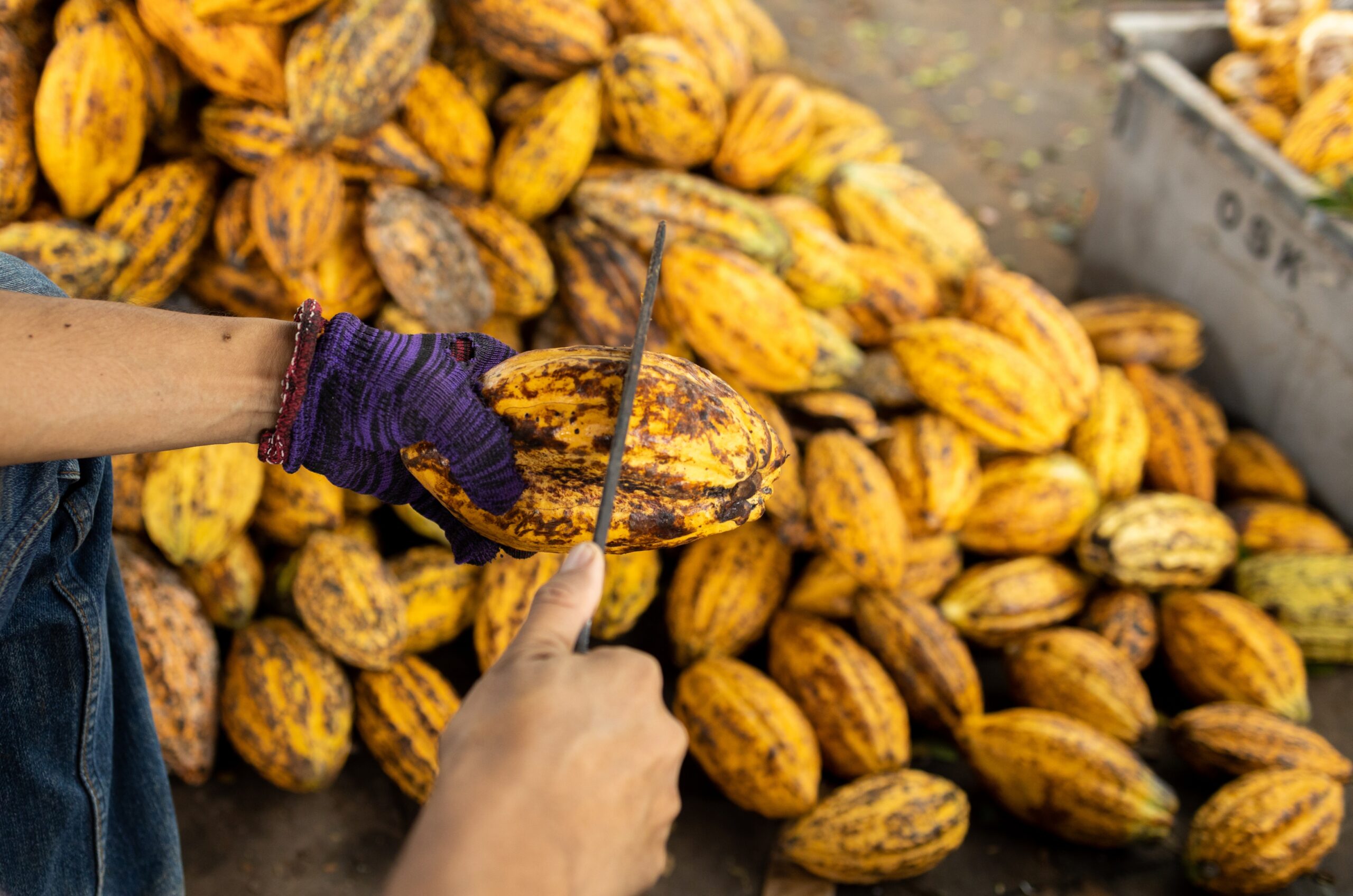
The production of cocoa butter for foods begins with the harvesting of cocoa pods, primarily grown in West Africa, South America, and parts of Asia. Africa, and particularly Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire, supplies over 60% of the world’s cocoa, making it the leading source of premium cocoa butter.
Step 1: Fermentation and Drying
Once the cocoa pods are harvested, the beans are removed and undergo fermentation. This crucial process develops the chocolate flavor and reduces bitterness. After fermentation, the beans are sun-dried to preserve quality and prepare them for milling.
Step 2: Roasting and Grinding
The dried beans are roasted to further enhance flavor. They are then cracked and ground into a thick paste known as cocoa liquor (or cocoa mass). This paste contains both cocoa solids and cocoa butter in natural form.
Step 3: Pressing the Cocoa Liquor
The cocoa liquor is placed under hydraulic pressure to separate the two main components:
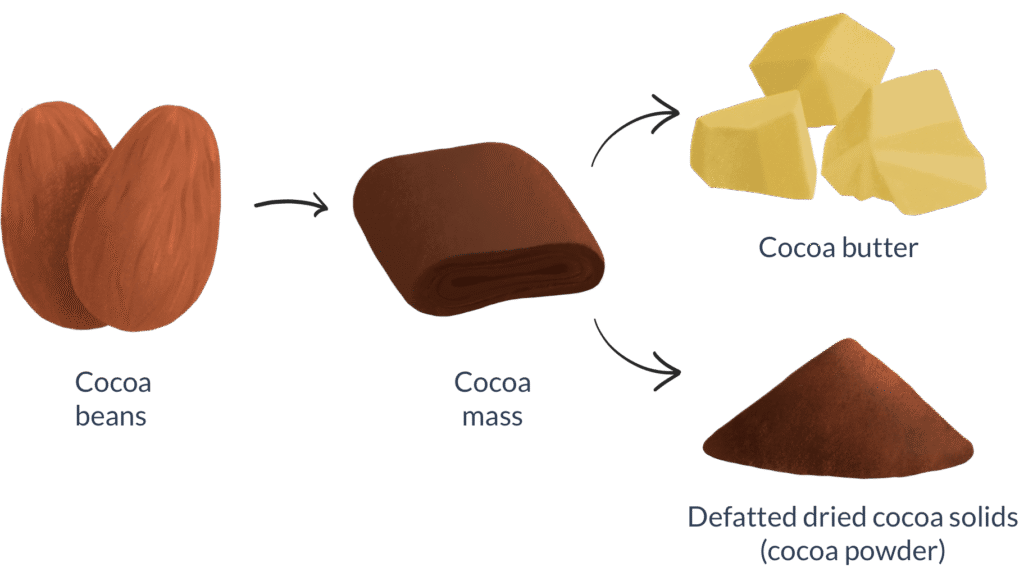
- Cocoa butter – the pale, edible fat.
- Cocoa powder – the dry, flavorful solid.
This separation allows manufacturers to use cocoa butter as a stand-alone food ingredient or recombine it in various chocolate products.
Step 4: Refining and Purification
For food-grade applications, the extracted cocoa butter undergoes refining and filtration. This ensures that the butter is free from impurities while retaining its natural aroma and mild chocolate flavor. In the case of organic cocoa butter, additional steps are taken to ensure that beans are grown without synthetic pesticides or chemicals, preserving purity from farm to final product.
Step 5: Packaging
Finally, cocoa butter is packed into blocks or chunks for commercial distribution. Standard packaging often includes 25kg cocoa butter cartons or blocks, while some suppliers also provide 5kg cocoa butter packs for smaller-scale buyers. This makes it accessible for both large manufacturers and artisanal chocolatiers.
Through this carefully controlled process, cocoa butter retains its natural stability, creamy texture, and premium quality, which are essential for chocolate making and other gourmet food applications.
Applications of Cocoa Butter in Food
Cocoa butter is one of the most versatile ingredients in the food industry. Its unique combination of flavor, texture, and melting properties makes it a favorite among chocolatiers, bakers, and food manufacturers worldwide.
- Chocolate Production
- Cocoa butter is the backbone of the chocolate industry.
- It gives chocolate its smooth texture, glossy finish, and “melt-in-the-mouth” sensation that no other fat can replicate.
- High-quality brands insist on using premium cocoa butter from Africa, especially cocoa butter Ghana, for its consistent flavor and stability.
- Confectionery and Desserts
- Used in truffles, pralines, ice creams, and gourmet desserts.
- Its mild chocolate aroma enhances sweetness without overpowering other flavors.
- Provides a creamy texture that appeals to consumers.
- Baking Industry
- Bakers use natural cocoa butter to improve dough texture, moisture retention, and flavor.
- It is particularly useful in croissants, cookies, and cakes, where richness and smoothness are desired.
- Health and Specialty Foods
- With rising demand for plant-based and clean-label products, organic cocoa butter has become a sought-after ingredient.
- Used in vegan chocolates, health bars, and dairy-free recipes.
- Its natural antioxidant content also makes it appealing for functional foods.
- Beverage Applications
- Increasingly used in hot chocolate blends, cocoa drinks, and flavored coffee products.
- Adds smoothness and a mild chocolate note.
Global Supply, Trade, and Market Prices of Cocoa Butter
- Global Supply Sources
The majority of food-grade cocoa butter comes from West Africa, particularly:
- Ghana – globally recognized for producing some of the best-grade cocoa butter, thanks to its high-quality beans and strict quality control systems.
- Côte d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) – the largest cocoa producer in the world, supplying both bulk and premium cocoa butter.
- Nigeria and Cameroon – also contribute significantly, though their production is smaller compared to Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire.
Beyond Africa, countries like Ecuador, Peru, and Indonesia also produce cocoa butter, often marketed as specialty or fine-flavor grades.
- Trade and Distribution
- Cocoa butter suppliers and manufacturers like Radad International typically export in bulk cocoa butter blocks of 25kg, packaged for shipping.
- Smaller quantities, such as 5kg cocoa butter packs, are distributed by retailers for artisanal or local use.
- Major buyers include chocolate factories, food companies, bakeries, and gourmet dessert brands.
- Regional Demand
- UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar are emerging markets with growing demand for premium cocoa butter. The rise in luxury confectionery, bakeries, and fine dining has made the Gulf region an attractive market for exporters.
- Europe and North America remain the largest consumers, driven by their well-established chocolate industries.
- Asia is quickly catching up, especially China, Japan, and India, where chocolate consumption is rising rapidly.
- Cocoa Butter Market Prices
The price of cocoa butter fluctuates depending on global cocoa supply, weather conditions, and demand.
- As of recent figures, premium quality cocoa butter from Africa trades at around USD 22,000 per metric ton (FOB, Ghana).
- Organic cocoa butter and certified fair-trade options are often priced higher due to stricter farming and certification costs.
- Bulk buyers typically negotiate contracts directly with cocoa butter manufacturers in Africa, while smaller buyers rely on distributors in UAE, Europe, or Asia.
- Bulk vs. Retail Trade
- Bulk cocoa butter is most commonly traded in 25kg cartons or blocks, ideal for industrial-scale chocolate production.
- Boutique chocolatiers or smaller food businesses often buy cocoa butter in 5kg packs, sourced from local cocoa butter sellers or specialized suppliers. Many tend to buy from Amazon as well.
How to Choose the Best Food-Grade Cocoa Butter
With so many cocoa butter suppliers and grades on the market, buyers need to know how to distinguish between standard, premium, and organic options. Whether you’re a chocolatier, a bakery owner, or a large-scale manufacturer, here are the key factors to consider when choosing the best food-grade cocoa butter.
- Origin of Cocoa Beans
- Ghanaian cocoa butter is highly regarded for its consistent quality, rich aroma, and smooth texture.
- Côte d’Ivoire offers bulk production at competitive rates, suitable for high-volume needs.
- Latin American origins like Ecuador and Peru are often marketed as fine-flavor cocoa butter, used in gourmet and specialty products.
- When sourcing cocoa butter from Africa, Ghana is often preferred for premium applications.
- Processing & Certification
- Ensure the cocoa butter is food-grade and processed according to international safety standards.
- Certifications to look out for include Organic, Fair-Trade, Rainforest Alliance, ISO, or HACCP.
- Certified suppliers often provide a higher level of transparency in sourcing and sustainability.
- Packaging & Supply Format
- 25kg cocoa butter blocks → Common for bulk buyers and manufacturers.
- 5kg cocoa butter packs → Practical for small-scale chocolatiers, bakeries, and testing batches.
- Buyers should check if the packaging ensures proper moisture resistance and preservation of aroma.
- Supplier Reliability
- Work only with trusted cocoa butter manufacturers, suppliers, or sellers who can guarantee consistent supply and quality.
- Many buyers prefer direct sourcing from Africa or established distributors in the UAE, Europe, or North America.
- For businesses in the Middle East, sourcing from cocoa butter suppliers like Radad International ensures faster delivery and lower logistics costs.
- Price vs. Quality Balance
- While the price of cocoa butter (approx. USD 22,000 per metric ton FOB Ghana) is an important factor, buyers must balance cost with quality.
- Low-cost cocoa butter may not always deliver the same flavor, melting profile, or shelf-life as premium African-origin butter.
- Always request samples or certifications before committing to bulk purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Cocoa Butter for Food
What is cocoa butter?
Cocoa butter is the natural fat extracted from cocoa beans during the chocolate-making process. It is pale-yellow, has a mild chocolate aroma, and is valued for its smooth texture and ability to melt at body temperature, making it essential for chocolate, confectionery, and baked goods.
Is cocoa butter the same as cocoa liquor or cocoa mass?
No. Cocoa liquor (or cocoa mass) is the ground paste of roasted cocoa nibs, which contains both cocoa solids and cocoa butter. Cocoa butter is the fat portion extracted from that liquor. Both are used in chocolate production but serve different functions.
What makes African cocoa butter so special?
Cocoa butter from Africa, especially Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire, is prized worldwide because African cocoa beans are known for their strong flavor, consistent quality, and superior fat content. This results in premium cocoa butter with excellent melting properties and aroma.
How is cocoa butter used in food?
Cocoa butter is widely used in:
- Chocolate production (gives smoothness and melt-in-mouth texture).
- Confectionery and desserts (enhances taste and texture).
- Baked goods (used as a natural fat).
- Ice creams and coatings (improves creaminess and stability).
What is the current price of cocoa butter?
The market price fluctuates depending on supply and demand. As of recent trade reports, premium quality cocoa butter from Ghana and West Africa is priced at around USD 22,000 per metric ton (FOB). Organic and certified options may cost more.
Can I buy cocoa butter in smaller quantities?
Yes. While bulk cocoa butter is usually sold in 25kg blocks for industrial buyers, smaller 5kg cocoa butter packs are available from specialized cocoa butter sellers for artisanal chocolatiers, bakeries, and small businesses.
Where can I source cocoa butter?
- Directly from cocoa butter manufacturers and suppliers in Africa (Ghana, Côte d’Ivoire).
- From global distributors in Europe and North America.
- Regional suppliers in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar, who cater to growing Middle Eastern demand.
How do I choose the best cocoa butter supplier?
Look for suppliers who:
- Offer certifications (Organic, ISO, Fair-Trade, HACCP).
- Provide consistent supply and competitive pricing.
- Package cocoa butter properly (to protect freshness and quality).
- Have a proven track record of supplying to food manufacturers.
What is the shelf life of cocoa butter?
Properly stored cocoa butter can last 2–5 years without going rancid, thanks to its natural stability and antioxidant properties. It should be kept in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Can cocoa butter be used in non-food industries?
Yes. Although this blog focuses on cocoa butter for food, it is also widely used in cosmetics, skincare, and pharmaceuticals because of its moisturizing and healing properties.
Is cocoa butter vegan and gluten-free?
Yes. Cocoa butter is naturally plant-based, dairy-free, and gluten-free, making it suitable for vegan, vegetarian, and gluten-free diets.






