The global chocolate industry is built on one essential agricultural product: raw cocoa beans. These small yet powerful seeds form the basis of every cocoa-derived product, from cocoa butter and powder to premium chocolate.
Africa remains the undisputed leader in global cocoa production, contributing over 70% of the world’s supply. Nations such as Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, and Sierra Leone have established themselves as dominant players in both volume and quality. The region’s favorable climate, fertile soil, and long-standing farming traditions make it the ideal environment for cultivating high-grade natural cocoa beans.
As demand for ethically sourced, traceable, and premium-quality cocoa increases, international buyers are turning more toward African cocoa bean suppliers and exporters. These suppliers not only deliver consistency in flavor and quality but also uphold sustainability and transparency across their supply chains.
This article provides a comprehensive guide for individuals and businesses seeking to purchase African cocoa beans in bulk. It explores the nature of raw cocoa, the leading producing regions, pricing considerations, and how to identify a trustworthy cocoa supplier or exporter.
Key Characteristics and Quality Indicators of Raw Cocoa Beans
Before engaging with cocoa suppliers or exporters, it is crucial for buyers to understand what defines raw cocoa beans and the factors that influence their quality. The quality of cocoa beans directly affects the flavor, texture, and value of the final product — whether it is chocolate, cosmetics, or beverages.
2.1 What Are Raw Cocoa Beans?
Raw cocoa beans are the seeds extracted from the pods of the Theobroma cacao tree. Once harvested, the beans undergo fermentation and drying, two critical processes that determine their final flavor and aroma.
These unroasted beans retain their natural antioxidants, minerals, and cocoa butter, making them ideal for processing into natural cocoa products such as cocoa powder, nibs, or butter. Buyers seeking bulk cocoa beans often prefer raw, well-fermented beans, as they preserve the natural composition and offer flexibility for further processing.
2.2 Key Quality Indicators in Cocoa Beans
When sourcing from African cocoa bean exporters, buyers should pay attention to the following quality parameters:
- Fermentation Level: Properly fermented beans (typically 5–7 days) develop deeper flavor notes and reduce bitterness.
- Moisture Content: Ideal moisture levels are between 6–7.5%. Higher moisture can lead to mold, while lower levels may cause brittleness.
- Bean Count: This refers to the number of beans per 100 grams. Premium beans usually range between 80–100 beans per 100g, indicating a good size and density.
- Flavor Profile: African cocoa beans typically display rich chocolate tones with regional variations — from nutty and earthy to fruity and floral.
- Defect Rate: High-quality beans should have minimal defects such as mold, germination, or insect damage.
2.3 Grades and Classification
Cocoa beans are commonly classified based on origin and quality grade:
- Standard Grade: Used for large-scale chocolate and confectionery manufacturing.
- Fine or Flavor Grade: Beans with distinctive flavor profiles, often used in premium and artisanal chocolate.
- Certified Organic or Fairtrade Cocoa: Grown under sustainable and ethical conditions, with traceability and certification provided by the cocoa bean exporter.
2.4 Importance of Proper Post-Harvest Handling
The handling of cocoa beans after harvest significantly affects their market value. Reputable cocoa bean suppliers ensure that fermentation, drying, sorting, and bagging are conducted under controlled conditions. Proper handling preserves the natural oils, prevents contamination, and maintains uniformity in color and aroma.
When purchasing African cocoa beans, buyers should request laboratory analysis or quality reports from exporters to confirm compliance with international standards such as ISO 2451:2017 for cocoa beans specification and grading.
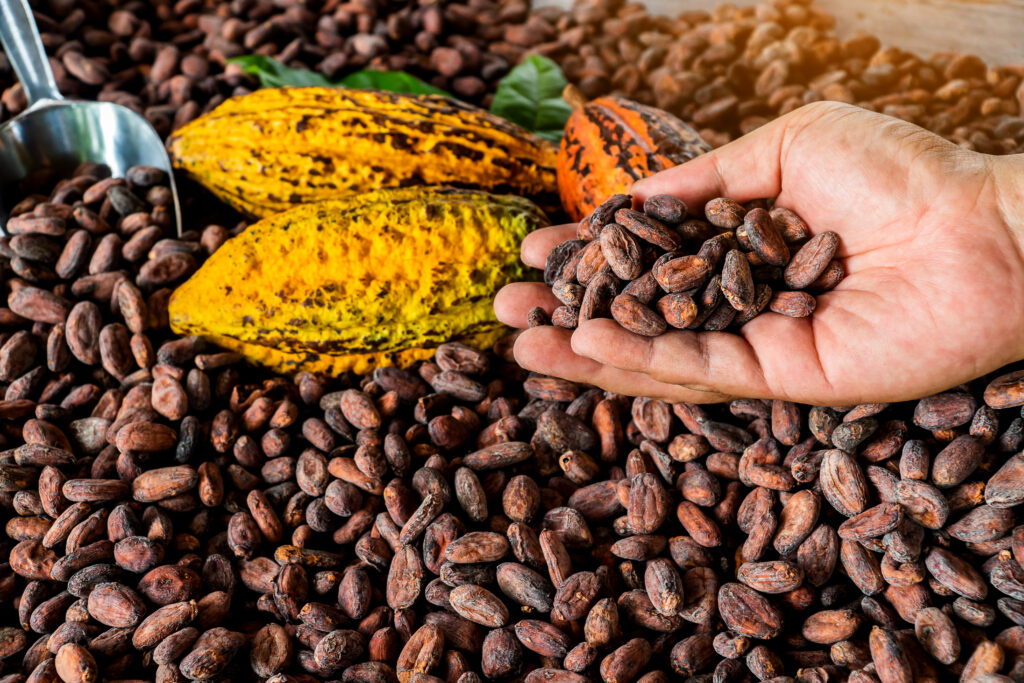

Major Cocoa-Producing Countries in Africa: Origins and Unique Characteristics
Africa’s reputation as the global hub for premium cocoa beans is rooted in both its agricultural heritage and favorable tropical conditions. Each producing nation contributes its own unique characteristics to the continent’s cocoa profile, resulting in diverse flavors and qualities that appeal to a wide range of buyers and manufacturers.
Below is an overview of the most significant African cocoa bean origins, their production capacity, and distinguishing attributes that international buyers should consider when sourcing.
3.1 Ivory Coast (Côte d’Ivoire) Cocoa Beans
Ivory Coast is the world’s leading cocoa producer, accounting for approximately 40% of global supply. The country’s cocoa sector is built on decades of farming experience, advanced post-harvest techniques, and strong export infrastructure.
Key Characteristics:
- Distinctively rich and earthy flavor, with mild acidity.
- High cocoa butter yield, making it ideal for chocolate and cosmetic applications.
- Consistent bean size and fermentation quality, preferred by major international chocolate manufacturers.
- Available in both conventional and certified (Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance) varieties.
Ivory Coast cocoa beans are often the standard reference for global buyers seeking stable supply, reliability, and scalability in bulk cocoa purchases. Many cocoa exporters from Ivory Coast operate through established cooperatives, ensuring quality control and traceability.
3.2 Ghana Cocoa Beans
Ghana is the second-largest cocoa producer globally and is widely regarded for its exceptional quality standards. Ghanaian cocoa beans are often considered the benchmark for flavor and purity in the international market.
Key Characteristics:
- Noted for their balanced chocolate flavor with a hint of fruitiness.
- Strict quality control by the Ghana Cocoa Board (COCOBOD) ensures uniform fermentation and drying practices.
- Typically graded as Grade I or II, suitable for both industrial and premium chocolate production.
Buyers seeking premium-grade African cocoa beans frequently turn to Ghana for its proven consistency and government-backed quality assurance.
3.3 Nigerian Cocoa Beans
Nigeria ranks among the top five cocoa-producing countries in the world and is a growing force in the African cocoa export market. The majority of Nigerian cocoa beans are produced in Ondo, Cross River, and Ekiti states.
Key Characteristics:
- Distinctive strong aroma with slightly bitter-sweet undertones.
- Well-fermented Forastero beans, known for durability during shipping and storage.
- Favorable fat content suitable for both cocoa butter extraction and chocolate manufacturing.
Nigeria’s cocoa industry has seen modernization in recent years, with exporters emphasizing traceability, improved fermentation facilities, and international certifications. This makes Nigerian cocoa bean suppliers a preferred choice for buyers looking for reliability combined with cost efficiency.
3.4 Cameroon Cocoa Beans
Cameroon has established itself as a key player in the West African cocoa trade. Its cocoa is primarily cultivated in the Central and Southwest regions, where soil fertility and humidity create optimal growing conditions.
Key Characteristics:
- Known for a robust, full-bodied flavor with fruity and slightly acidic notes.
- High cocoa butter yield, often used for blending with beans from other origins.
- Increasing supply of fine-flavor cocoa through local cooperatives and organic farming initiatives.
Many boutique chocolate producers and specialty manufacturers source from Cameroon cocoa bean exporters due to the distinct character and versatility of the beans.
3.5 Sierra Leone Cocoa Beans
Though smaller in output, Sierra Leone has gained attention for its organic and sustainable cocoa farming. Many farms operate under smallholder systems with minimal chemical intervention, resulting in natural cocoa beans that appeal to the growing organic chocolate segment.
Key Characteristics:
- Naturally low-acidity, sweet flavor, and clean aroma.
- Often certified organic or Rainforest Alliance, with traceable origins.
- Sourced primarily by specialty buyers and niche chocolate brands.
Sierra Leone cocoa exporters are steadily expanding their global presence, catering to importers who prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing over large-scale volume.
3.6 Comparative Overview
| Origin Country | Key Flavor Notes | Cocoa Butter Yield | Common Certifications | Ideal For |
| Ivory Coast | Earthy, balanced | High | Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance | Industrial chocolate, cosmetics |
| Ghana | Smooth, fruity | Moderate | COCOBOD-certified | Premium chocolate, confectionery |
| Nigeria | Aromatic, strong | High | Organic, Fairtrade | Mass-market and artisanal chocolate |
| Cameroon | Fruity, robust | High | Cooperative-certified | Specialty and blended chocolates |
| Sierra Leone | Sweet, mild | Moderate | Organic, Fairtrade | Organic and niche chocolate production |
Each origin brings unique advantages to the cocoa trade. For buyers, diversifying sourcing across multiple African regions can help balance flavor diversity, supply stability, and cost efficiency.

How to Choose the Right Cocoa Bean Supplier or Exporter
Selecting the right cocoa bean supplier or exporter is a crucial step for businesses that rely on consistent quality, traceable sourcing, and timely delivery. Whether you are a chocolate manufacturer, confectionery company, or bulk importer, your choice of supplier directly affects product quality, cost efficiency, and brand reputation.
Below are key factors to consider when choosing a reliable African cocoa supplier or exporter.
4.1 Verify Quality Standards and Certifications
Quality assurance is the foundation of any successful cocoa trade partnership. Reputable cocoa exporters adhere to internationally recognized standards and certifications that guarantee safety, consistency, and sustainability.
When evaluating suppliers, request documentation related to:
- ISO Certification (e.g., ISO 2451:2017 for cocoa bean specification)
- HACCP or Food Safety Management Systems
- Fairtrade and Rainforest Alliance Certifications
- Organic Certification (where applicable)
These certifications indicate that the cocoa beans are processed and handled under regulated conditions that meet global trade standards. Certified African cocoa bean exporters also ensure compliance with buyer-specific requirements, such as residue limits, moisture control, and packaging protocols.
4.2 Assess Traceability and Transparency
Modern buyers increasingly prioritize traceability, the ability to track cocoa beans from the farm to the final shipment. Reliable suppliers provide full transparency about:
- The region of origin (e.g., Nigeria, Ivory Coast, or Ghana)
- The farming cooperatives or producer networks involved
- Harvest dates and processing methods
- The storage and shipment process
Traceable sourcing not only ensures quality control but also supports ethical and sustainable farming practices. Working with traceable African cocoa bean suppliers enhances buyer confidence and simplifies certification audits for end products.
4.3 Request Product Samples and Testing Reports
Before making any large purchase, request sample shipments and third-party laboratory test reports from the exporter. Testing verifies crucial metrics such as:
- Bean count (number of beans per 100 grams)
- Fermentation percentage (degree of flavor development)
- Moisture content (ideally below 7.5%)
- Fat content and purity
Sampling also allows buyers to conduct sensory analysis, examining the aroma, color, and taste profile of the beans. Leading cocoa bean exporters in Africa often provide both physical and digital quality reports, giving buyers detailed insight into the product’s specifications.
4.4 Evaluate Supplier Experience and Export Capacity
The experience of a cocoa supplier plays a significant role in ensuring reliable supply and smooth logistics. When shortlisting potential exporters, consider:
- Years of operation in the cocoa export industry
- Export volume capacity (ability to handle small and bulk orders)
- International client references and past trade history
- Partnerships with shipping lines and freight forwarders
Established African cocoa exporters usually maintain strong logistical networks, allowing them to deliver shipments efficiently while managing documentation, customs clearance, and international compliance.
4.5 Compare Pricing and Contract Terms
While price competitiveness is important, it should not be the only deciding factor. Cocoa prices are influenced by global market fluctuations, quality grades, and shipping costs. Reputable suppliers maintain transparent pricing models and offer clear contract terms, including:
- Minimum order quantity (MOQ)
- Payment terms (e.g., Letter of Credit, TT)
- Delivery timelines (FOB, CIF, or EXW options)
- Quality and weight dispute resolution policies
Working with a supplier that provides clear documentation, consistent communication, and flexibility in negotiation ensures smoother transactions and long-term cooperation.
4.6 Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
An increasing number of buyers are aligning their sourcing policies with sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) objectives. Leading African cocoa exporters are responding by:
- Supporting farmer cooperatives and fair compensation systems.
- Promoting child-labor-free supply chains.
- Encouraging environmentally responsible farming techniques.
- Offering certified sustainable cocoa that meets EU and U.S. import requirements.
Partnering with ethical suppliers not only enhances brand reputation but also contributes to the long-term viability of Africa’s cocoa industry.
4.7 Communication and Support
A professional supplier maintains prompt communication, transparency, and ongoing support. Responsiveness to inquiries, accurate documentation, and post-shipment follow-ups are indicators of reliability.
For new buyers, it is advisable to begin with smaller test orders before scaling to bulk purchases. This allows time to evaluate both the product quality and the efficiency of the supplier’s operations.
By carefully assessing these factors, buyers can build long-term partnerships with dependable African cocoa bean exporters who deliver consistent quality, competitive pricing, and ethical sourcing practices.

Types of Cocoa Beans and Their Market Applications
The cocoa industry recognizes three main varieties of cocoa beans — Forastero, Criollo, and Trinitario. Each variety possesses distinct flavor characteristics, cultivation patterns, and commercial value. Understanding these differences helps buyers source the most suitable raw cocoa beans for their intended use — whether for chocolate manufacturing, cosmetics, or beverage production.
5.1 Forastero Cocoa Beans
Forastero cocoa beans make up nearly 80–85% of global cocoa production and are primarily grown in West Africa, particularly in Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, and Cameroon.
These beans are known for their robust flavor, high yield, and resistance to pests and diseases. They tend to produce a strong, earthy taste, making them the preferred choice for mass-market chocolate and cocoa powder production.
Key Features:
- Origin: Predominantly Africa and parts of South America
- Flavor: Bold, full-bodied, and slightly bitter
- Usage: Main ingredient in commercial chocolate, cocoa butter, and cocoa powder
- Advantage: Stable supply, affordable price, and consistent quality
Buyers seeking bulk cocoa beans for industrial processing or large-scale manufacturing often choose Forastero due to its cost-effectiveness and uniformity.
5.2 Criollo Cocoa Beans
Criollo cocoa beans are considered the finest and rarest variety in the world. Originally cultivated in Central and South America, Criollo is now also grown in smaller quantities across select African regions.
These beans produce chocolate with delicate aroma, low acidity, and complex flavor notes, often described as floral, nutty, and slightly caramel-like. Due to their limited yield and sensitivity to climate and disease, Criollo beans are typically more expensive and primarily used in luxury chocolate production.
Key Features:
- Origin: Latin America, limited cultivation in Africa
- Flavor: Refined, aromatic, and less bitter
- Usage: Premium chocolate, artisan confectionery, and gourmet cocoa products
- Advantage: Exceptional taste profile and high market value
Buyers sourcing premium African cocoa beans for specialty chocolate or boutique brands may seek Criollo or Criollo-hybrid varieties from carefully selected suppliers.
5.3 Trinitario Cocoa Beans
The Trinitario variety is a hybrid of Criollo and Forastero, offering the best of both worlds, disease resistance from Forastero and fine flavor from Criollo. It was first developed on the island of Trinidad (hence the name) and has since spread to various tropical regions, including West and Central Africa.
Trinitario beans are widely appreciated for their balanced flavor, pleasant aroma, and moderate acidity, making them suitable for both mass-market and premium chocolate products.
Key Features:
- Origin: Trinidad, now cultivated across Africa and the Caribbean
- Flavor: Complex, aromatic, and well-rounded
- Usage: Mid-range to high-end chocolate, specialty blends, and cocoa butter extraction
- Advantage: Versatility, quality consistency, and reliable yield
Because of their versatility, Trinitario cocoa beans are increasingly popular among buyers seeking a blend of quality and affordability for diverse product applications.
5.4 Specialty and Organic Cocoa Beans
Beyond the traditional classifications, there is growing global demand for organic and sustainably farmed cocoa beans. African exporters have begun meeting this demand by offering:
- Organic-certified cocoa beans grown without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides.
- Fairtrade cocoa ensuring fair compensation for farmers.
- Single-origin cocoa, which allows brands to highlight traceable and unique flavor profiles tied to a specific region, such as Ivory Coast cocoa beans or Nigerian cocoa beans.
These specialty beans cater to premium brands in Europe, North America, and Asia seeking authenticity and ethical production credentials.
5.5 Market Applications of Raw Cocoa Beans
Cocoa beans are remarkably versatile, serving multiple industries beyond chocolate manufacturing. Here’s how they are typically used:
- Chocolate and Confectionery Industry
- The largest consumer of African cocoa beans.
- Uses both Forastero and Trinitario beans for chocolate bars, truffles, and desserts.
- Cosmetic and Skincare Industry
- Cocoa butter, derived from beans, is a key ingredient in moisturizers, soaps, and lip balms.
- Raw cocoa is also used in natural skincare products for its antioxidant properties.
- Beverage Industry
- Ground natural cocoa beans are processed into cocoa powder for use in beverages and nutritional supplements.
- Nutraceutical and Health Sector
- Cocoa extracts rich in flavonoids are used in health supplements, known for improving cardiovascular health and cognitive function.
As global demand for natural, traceable, and health-beneficial ingredients grows, African cocoa bean exporters are well-positioned to meet the needs of these diverse industries.
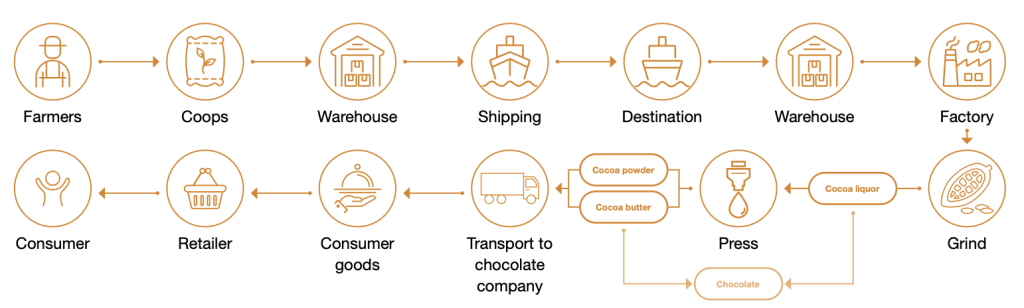
The African Cocoa Supply Chain and Export Process
The journey of raw cocoa beans from African farms to international buyers involves several carefully managed stages. Each step, from harvesting to shipping, plays a critical role in determining the flavor, quality, and value of the final product.
Understanding this process is essential for anyone seeking to buy or import African cocoa beans in bulk, as it ensures informed decisions when selecting suppliers or exporters.
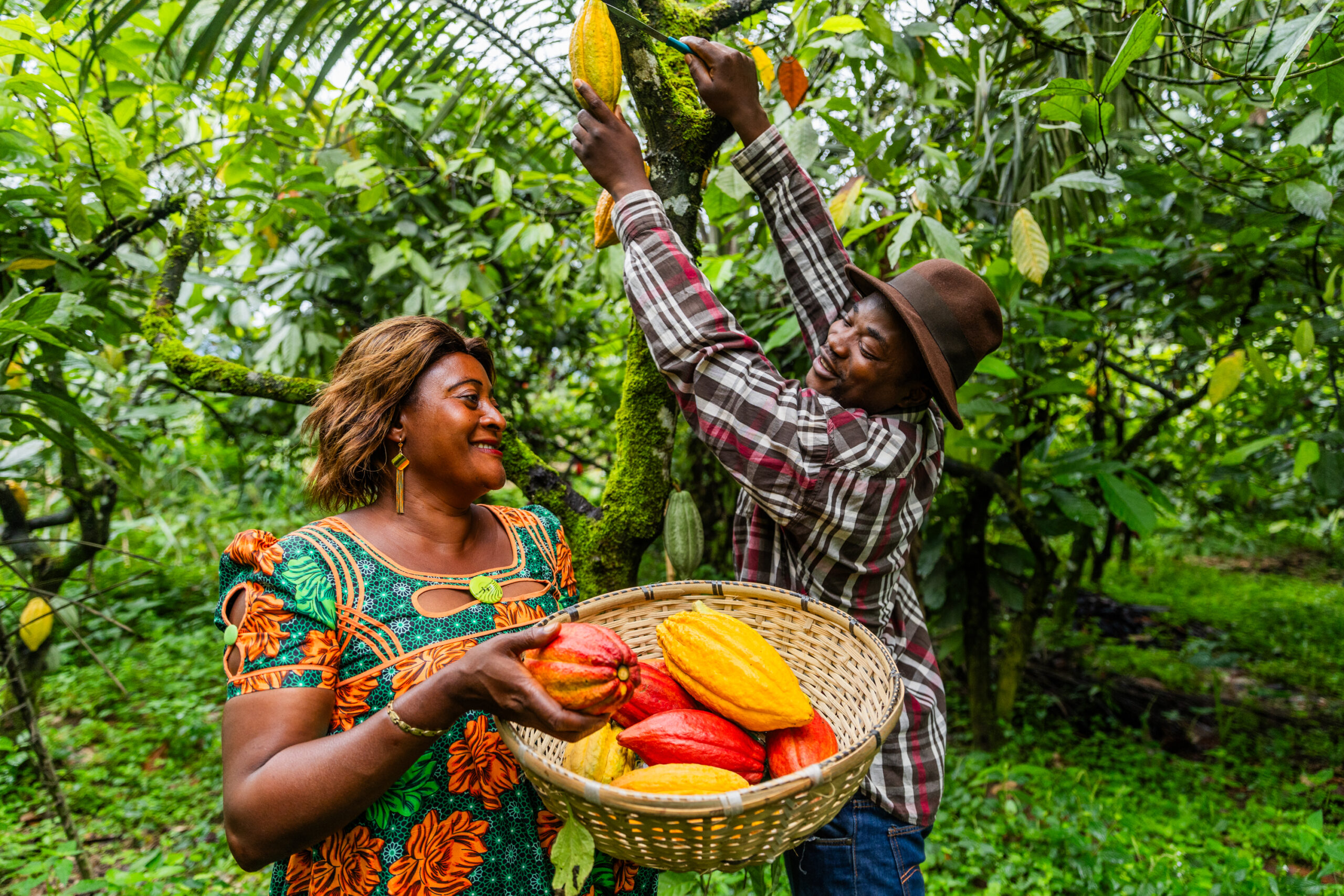
6.1 Harvesting
Cocoa harvesting typically occurs twice a year across major African producing countries such as Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, and Cameroon. The ripe cocoa pods, which grow directly on the trunk and branches of the tree, are handpicked using machetes or specialized knives.
Farmers usually identify mature pods by their color change, from green to yellow, red, or orange, depending on the variety. Proper harvesting is crucial, as premature or delayed collection can negatively affect bean flavor and fermentation quality.
After harvesting, the pods are split open to extract the wet cocoa beans, which are still covered in a sweet, sticky pulp.
6.2 Fermentation (Developing the Flavor Profile)
Fermentation is the most important stage in cocoa processing. During this period, the beans undergo a natural biochemical transformation that develops the characteristic cocoa flavor and aroma.
In Africa, fermentation usually takes place in wooden boxes or banana leaf-covered heaps, lasting between 5 to 7 days. The heat generated during fermentation removes bitterness, enhances color, and initiates the flavor compounds essential for chocolate production.
Properly fermented African cocoa beans are brown in color, have a pleasant cocoa scent, and contain reduced moisture, ideal for drying.
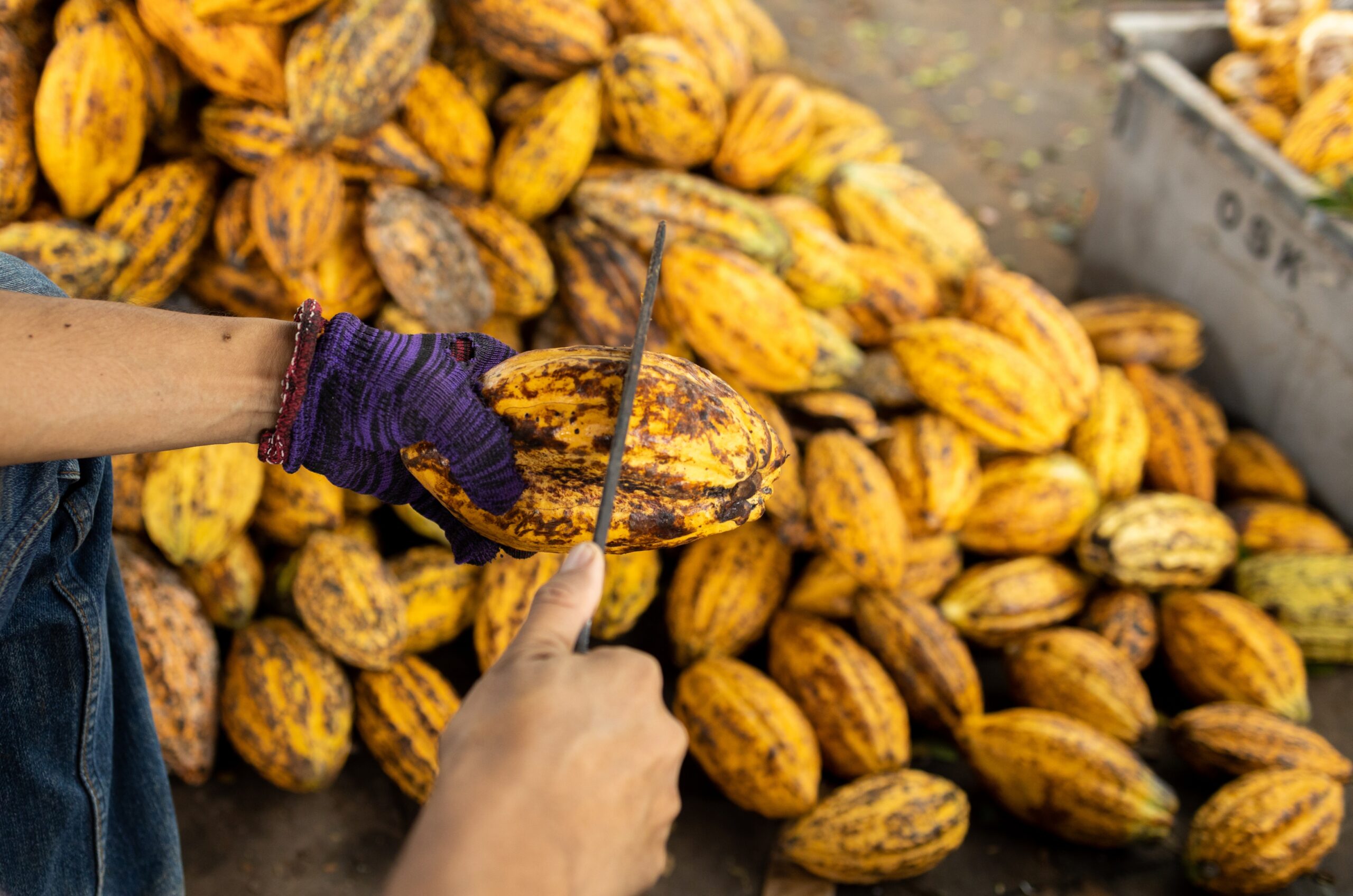
6.3 Drying
Once fermentation is complete, the beans are dried under the sun on raised mats or concrete platforms for 5 to 10 days, depending on weather conditions.
Drying reduces the moisture content to below 7.5%, preventing mold growth and ensuring safe long-distance shipping. During drying, beans are turned regularly to achieve even dehydration.
Some exporters also use mechanical dryers during the rainy season to maintain consistency. Proper drying ensures the beans remain in natural, high-quality condition until export.
6.4 Sorting and Grading
Before export, cocoa beans are sorted and graded based on internationally recognized standards. Factors considered include:
- Bean size and uniformity
- Moisture content
- Fermentation level
- Defect rate (broken or moldy beans)
Grading ensures buyers receive consistent quality. The most common grades include Grade I (Premium) and Grade II (Standard Export Quality). Premium buyers, especially in Europe and Asia, often prefer well-fermented, low-defect African cocoa beans for high-end chocolate and confectionery production.
6.5 Packaging and Storage
After grading, beans are packed into jute or sisal bags, typically weighing 60 to 65 kilograms each. These natural fibers allow air circulation, preventing moisture accumulation and spoilage.
The bags are stored in ventilated warehouses before shipment. Exporters ensure that storage areas are kept dry, pest-free, and cool to preserve freshness and aroma. Proper packaging and storage directly impact the longevity and quality of the cocoa beans upon arrival at their destination.
6.6 Export Documentation and Shipping
The export process requires several essential documents to comply with international trade regulations. Typical paperwork includes:
- Commercial Invoice and Packing List
- Certificate of Origin
- Phytosanitary Certificate (verifying that the product is pest-free)
- Quality and Weight Certificate
- Bill of Lading or Airway Bill
Most African cocoa exporters ship products via sea freight (FOB or CIF terms), depending on buyer preferences. Larger exporters often maintain partnerships with freight forwarders and inspection agencies to ensure timely and secure deliveries.
Efficient logistics and clear documentation are vital for maintaining buyer trust and smooth customs clearance in destination markets.
6.7 The Role of Technology and Sustainability
Modern African cocoa bean suppliers increasingly integrate technology and sustainability into their operations.
- Digital traceability systems allow buyers to track cocoa back to specific farms.
- Sustainability programs ensure farmers receive fair compensation and adopt eco-friendly practices.
- Blockchain tracking and QR-coded certification systems are emerging as tools for transparency.
These advancements not only enhance product credibility but also align with global buyers’ expectations for ethical and responsible sourcing.
The African cocoa export process reflects a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern trade efficiency. From smallholder farmers to major exporters, every participant contributes to maintaining Africa’s reputation as the world’s leading source of high-quality natural cocoa beans.
Pricing, Market Trends, and Global Demand for African Cocoa Beans
The global cocoa market is one of the most dynamic and closely monitored agricultural sectors in the world. Prices fluctuate due to a combination of climatic conditions, global demand, production volumes, and economic factors.
For buyers seeking raw African cocoa beans, understanding these trends provides a significant advantage when sourcing or negotiating supply contracts.
7.1 Global African Cocoa Market Overview
Cocoa is among the top five most traded agricultural commodities globally, with an estimated market value exceeding $130 billion annually when considering chocolate and cocoa-based products.
Africa contributes over 70% of global cocoa production, led by:
- Ivory Coast: ~2.2 million metric tons annually
- Ghana: ~800,000 to 1 million metric tons
- Nigeria: ~340,000 metric tons
- Cameroon: ~300,000 metric tons
- Sierra Leone and others: growing contributions
This dominance makes African countries the cornerstone of the international cocoa supply chain, directly influencing global prices and quality standards.
7.2 Cocoa Bean Pricing Structure
The price of raw cocoa beans depends on several key factors:
- Global Commodity Prices – Cocoa prices are typically benchmarked on the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE) in London and New York. Market rates fluctuate daily based on global supply-demand balances, weather patterns, and economic conditions.
- Origin and Quality – Premium beans from Ivory Coast, Ghana, or Nigeria may command higher prices due to superior fermentation, traceability, and certification. Organic cocoa or single-origin African cocoa beans also attract premium pricing.
- Certification and Processing – Beans that are Fairtrade-certified, Rainforest Alliance-approved, or organic-certified tend to sell at a premium of 10–30% above standard export rates due to ethical and sustainability assurance.
- Logistics and Incoterms – Prices vary based on whether they are quoted as FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance & Freight), or EXW (Ex Works). Buyers must consider transportation, insurance, and port handling costs when calculating landed prices.
- Currency Exchange Rates As most cocoa transactions are conducted in U.S. dollars, fluctuations in local currencies (e.g., CFA franc, naira) can impact export costs and pricing flexibility.
7.3 Typical Price Ranges (Indicative)
While prices change frequently, as of recent data (2025 estimates):
- Standard bulk cocoa beans: USD $6,500 – $7,500 per metric ton
- Premium fermented beans: USD $8,200 – $8,400 per metric ton
- Organic or certified beans: USD $8,500 – $9,500 per metric ton
- Fine-flavor or Criollo beans: USD $9,000+ per metric ton
These rates vary depending on quantity, contract duration, and logistics arrangements. Buyers dealing with reputable African cocoa bean exporters like Radad International can often negotiate better long-term rates with consistent supply agreements.
7.4 Global Demand Trends
Demand for cocoa and chocolate products continues to grow steadily, especially in emerging markets across Asia and the Middle East. At the same time, Western Europe and North America remain the largest importers of raw cocoa beans, accounting for nearly 65% of global imports.
Several trends currently shape the global cocoa trade:
- Rising Demand for Ethical Cocoa Brands increasingly prioritize sustainably sourced cocoa, pushing exporters to offer traceable and certified beans.
- Growth of Artisan and Craft Chocolate The global shift toward premium, small-batch chocolate has led to higher demand for single-origin African cocoa beans known for distinctive flavor notes.
- Health and Wellness Market Expansion The nutritional benefits of cocoa (antioxidants, flavonoids, mood enhancement) are driving new demand in health foods and nutraceuticals.
- Digital Trade and Transparency Buyers now expect real-time shipment tracking, digital certification, and blockchain-based traceability from their cocoa suppliers.
- Sustainability Investments Cocoa exporters are adopting agroforestry models, waste recycling, and community support initiatives to ensure long-term crop sustainability and brand credibility.
7.5 The Impact of Climate and Supply Disruptions
Cocoa is highly sensitive to weather conditions. Droughts, irregular rainfall, or pest infestations can reduce yields and trigger price spikes. Similarly, logistical disruptions, port congestion, or political instability in key producing regions can influence short-term supply and cost.
To mitigate such risks, international buyers often diversify sourcing, purchasing from multiple African origins (e.g., Nigeria, Cameroon, Sierra Leone) to ensure consistent availability.
7.6 Opportunities for Buyers and Investors
For buyers and traders, Africa presents significant opportunities:
- Direct sourcing from producers reduces intermediary costs.
- Growing investment in processing facilities allows exporters to offer semi-finished cocoa products like butter and powder.
- Partnerships with farmer cooperatives ensure better quality control and traceability.
- Favorable trade policies and logistics networks (especially through ports like Abidjan, Lagos, and Douala) enhance export efficiency.
Engaging with credible African cocoa bean suppliers offers access to both competitive pricing and ethically sourced, high-grade cocoa aligned with modern market expectations.
The African cocoa market remains the lifeblood of the global chocolate industry, resilient, evolving, and full of opportunity. With strategic sourcing, transparent partnerships, and awareness of market trends, buyers can secure a sustainable and profitable cocoa supply chain for years to come.

Why Choose African Cocoa Beans and Trusted Exporters Like Radad International
The global cocoa trade continues to thrive, and Africa remains its undisputed heart. From the lush plantations of Ivory Coast to the fertile soils of Nigeria, Cameroon, and Sierra Leone, the continent produces the world’s finest natural cocoa beans, prized for their rich flavor, strong aroma, and consistent quality.
For any buyer, whether a small-scale chocolatier or a multinational food manufacturer, sourcing directly from reliable African cocoa bean exporters ensures not only access to premium products but also alignment with ethical, traceable, and sustainable practices.
8.1 Why African Cocoa Beans Stand Out
- Superior Quality and Distinct Flavor African cocoa beans, especially those from Ivory Coast, Ghana, and Nigeria — are recognized for their full-bodied, well-fermented profiles that form the foundation of most global chocolate brands.
- Consistency and Volume Africa’s vast production network and experienced farming communities guarantee consistent supply in both small and large volumes, making it ideal for bulk buyers.
- Sustainability and Fair Trade The region has made significant strides toward sustainable farming, traceability, and fair farmer compensation, ensuring that each batch of raw cocoa beans contributes to both quality and community impact.
- Competitive Pricing Thanks to scale, expertise, and favorable agricultural conditions, African cocoa suppliers offer some of the most competitive prices in the global market without compromising quality.
8.2 Radad International — A Trusted Partner in African Cocoa Exports
Among the emerging leaders in Africa’s cocoa export industry, Radad International has built a strong reputation as a premium supplier of raw cocoa beans and other agricultural commodities.
With a focus on quality, transparency, and reliability, Radad International works directly with farming cooperatives across Nigeria, Ivory Coast, Cameroon, and Sierra Leone to ensure buyers receive high-grade cocoa that meets international standards.
Key strengths of Radad International include:
- Premium Quality Assurance: Each shipment undergoes strict quality checks, grading, and certification before export.
- Ethical and Sustainable Sourcing: The company maintains close relationships with local farmers, promoting fair trade, sustainable practices, and traceability from farm to port.
- Flexible Export Solutions: Radad International provides both bulk cocoa beans and custom shipment options, catering to diverse buyer needs across Europe, Asia, and North America.
- Global Logistics Network: With efficient handling, clear documentation, and partnerships with top freight carriers, they ensure on-time delivery and smooth customs clearance.
- Customer-Centric Approach: The company emphasizes communication, reliability, and long-term partnership, values that make it a trusted name among African cocoa bean exporters.
By combining local expertise with international trade experience, Radad International helps buyers confidently source African cocoa beans that meet both quality and sustainability expectations.
The story of cocoa is one of passion, craftsmanship, and global connections. Africa’s fertile lands and hardworking farmers continue to supply the world with cocoa beans that define the taste of chocolate itself.
For anyone seeking bulk cocoa beans, natural African cocoa, or a long-term partnership built on trust and quality — Africa remains the ideal origin, and Radad International stands out as a dependable partner to help you achieve your sourcing goals.
Whether you’re a chocolate manufacturer, ingredient supplier, or importer seeking consistency and quality, choosing African cocoa means investing in excellence, and with the right exporter, you gain far more than a product; you gain a partnership built on values, transparency, and growth.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are raw cocoa beans?
Raw cocoa beans are the fermented and dried seeds of the cocoa tree (Theobroma cacao). These beans are the primary ingredient used in the production of chocolate, cocoa powder, and cocoa butter. When unprocessed, natural cocoa beans retain all their nutrients and antioxidants, making them valuable for food, cosmetic, and health industries.
Why are African cocoa beans highly valued globally?
Africa accounts for more than 70% of the world’s cocoa production, with Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, and Cameroon leading the market. African cocoa beans are known for their rich flavor profile, consistent quality, and high butter content, which makes them ideal for both mass-market chocolate and premium artisan products. Additionally, many African cocoa exporters now emphasize traceability, sustainability, and fair trade, increasing their appeal to international buyers.
What are the main varieties of cocoa beans produced in Africa?
The three primary varieties are:
- Forastero – The most common type, known for its bold, earthy flavor and high yield.
- Criollo – A rare, fine-flavor variety prized for its delicate aroma and mild taste.
- Trinitario – A hybrid of Forastero and Criollo, combining robust production with refined flavor.
Most bulk cocoa beans from Africa belong to the Forastero or Trinitario varieties, ideal for commercial processing.
What is the difference between raw cocoa and processed cocoa?
Raw cocoa refers to the unroasted, natural form of cocoa beans, usually fermented and dried but not heat-treated.
Processed cocoa, on the other hand, has been roasted, ground, or refined into products like cocoa powder or butter.
Buyers who seek raw African cocoa beans typically prefer them for chocolate manufacturing, nutraceuticals, or cosmetic production, as they can control the level of processing and flavor development themselves.
What countries in Africa produce the best quality cocoa beans?
The leading producers include:
- Ivory Coast (Côte d’Ivoire) – The world’s largest cocoa exporter.
- Ghana – Known for its well-fermented and consistently graded beans.
- Nigeria – Valued for rich flavor and increasing organic cocoa output.
- Cameroon – Offers diverse flavor profiles suitable for both mass and premium chocolate.
- Sierra Leone – An emerging source of traceable, high-quality natural cocoa beans.
Each origin offers unique flavor characteristics, giving buyers the flexibility to blend or single-source beans depending on their product goals.
How can I buy cocoa beans in bulk from Africa?
To buy bulk cocoa beans, it’s important to:
- Identify certified suppliers or exporters — look for companies with verifiable trade history and export licenses.
- Request product specifications — including moisture level, fermentation grade, and bean count.
- Ask for samples or lab reports to confirm quality.
- Negotiate terms and Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF).
- Confirm export documentation such as Certificate of Origin, Quality Certificate, and Phytosanitary Certificate.
Trusted companies like Radad International simplify this process by offering full documentation, logistics support, and quality assurance for all cocoa exports.
What is the price of cocoa beans per ton?
Prices vary depending on quality, certification, and market conditions. As of recent trade estimates:
- Standard bulk cocoa beans: $2,500 – $3,500/MT
- Premium fermented cocoa beans: $3,600 – $4,500/MT
- Organic or certified cocoa beans: $4,500 – $5,500/MT
- Fine-flavor (Criollo) beans: $6,000+/MT
Buyers working with established African cocoa bean exporters like Radad International can negotiate stable long-term pricing based on quantity and supply consistency.
How do I ensure the quality of cocoa beans before purchase?
Before finalizing a bulk order, always:
- Request physical samples and third-party lab test reports.
- Verify the supplier’s certifications (ISO, HACCP, Fairtrade, Organic).
- Check for moisture content (<7.5%), fermentation percentage, and bean uniformity.
- Ask for recent export documentation and photos of current stock.
Radad International, for instance, provides buyers with detailed quality reports and supports independent inspection before shipment.
What documents are required for cocoa export and import?
Typical export documents include:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Origin
- Phytosanitary Certificate
- Quality and Weight Certificate
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Airway Bill These ensure compliance with international trade and food safety regulations.
Are African cocoa beans suitable for organic or Fairtrade sourcing?
Yes. Many African cocoa suppliers now provide organic-certified and Fairtrade cocoa beans. These beans are cultivated without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, ensuring both environmental sustainability and farmer welfare. Exporters like Radad International work with certified cooperatives to provide traceable, ethically sourced cocoa for eco-conscious brands.
Can I order small quantities for testing before bulk purchase?
Absolutely. Most reputable exporters allow sample shipments or small trial orders (often 50–500 kg) for evaluation before full-scale contracts. This helps buyers confirm quality, flavor profile, and logistics efficiency before committing to bulk orders.
How long does shipping from Africa take?
Shipping time depends on the destination and shipping method:
- To Europe: Approximately 3–5 weeks by sea
- To Asia or the Middle East: 4–6 weeks
- To North America: 5–7 weeks Exporters like Radad International handle all logistics, documentation, and customs coordination to ensure on-time delivery.
What is the shelf life of raw cocoa beans?
When properly dried and stored, raw cocoa beans can last 12–24 months without losing quality. They should be stored in cool, dry, and well-ventilated conditions, ideally in jute or sisal bags to prevent moisture buildup.
Are cocoa beans from Africa traceable?
Yes. Many exporters now provide full traceability through digital tracking and certification systems. Buyers can trace cocoa back to specific farms or cooperatives, ensuring transparency, quality assurance, and compliance with global sustainability standards.
Why choose Radad International as your cocoa supplier?
Radad International is a leading African cocoa bean exporter known for:
- Premium-grade natural cocoa beans sourced from West and Central Africa
- Strict quality control and international certifications
- Transparent and ethical sourcing
- Competitive bulk pricing and flexible shipping
- Personalized support for buyers across Europe, Asia, and North America
Whether you need Nigerian cocoa beans, Ivory Coast cocoa beans, or a bulk shipment from multiple African origins, Radad International ensures reliability, quality, and professionalism in every transaction.
How do I contact Radad International for inquiries or orders?
You can reach Radad International directly through their official communication channels for inquiries about bulk cocoa beans, samples, or partnership opportunities. You can email info@radadinternational.com or call +971522501039 Their export team provides prompt assistance with quotations, documentation, and shipping schedules tailored to your region and order size. For more, click here to get to us
When sourcing African cocoa beans, working with a transparent and experienced partner like Radad International ensures peace of mind, product consistency, and global-standard quality. Whether you are expanding your chocolate production, launching a new brand, or importing raw cocoa for processing, Africa remains the best origin, and Radad International is a name you can trust.







One Response
This is a very elucidating, exquisite, informative, educative presentation. It has opened one’s eyes to an area one had not taken interest in before. Coming from your company makes it very attractive, as a company that knows the know-how, to confidently work with as partners in the cocoa beans export business which we are just being introduced to by a request. Thanks for the enlightenment.